Mastering Java ArrayList Reverse: Your Ultimate Guide To Flipping Arrays Like A Pro
So, you're here to learn about Java ArrayList reverse? Well, you're in the right place, my friend. Reversing an ArrayList in Java is one of those skills that every developer should have up their sleeve. Whether you're building a simple app or tackling complex algorithms, knowing how to reverse an ArrayList can save your bacon more times than you'd think. Let's dive into why this skill is so crucial and how it can elevate your coding game.
Imagine you're working on a project where data needs to be displayed in reverse order. Maybe you're dealing with a stack of tasks, a playlist, or even a list of users. Suddenly, you realize you need to flip that ArrayList around—and fast. This is where Java ArrayList reverse comes into play. It's not just a random feature; it's a tool that can streamline your workflow and make your code cleaner, faster, and more efficient.
Now, if you're new to Java or ArrayLists in general, don't worry. This guide is designed to walk you through everything you need to know about reversing ArrayLists. From basic methods to advanced techniques, we'll cover it all. So grab a cup of coffee, sit back, and let's get started on this coding adventure!
Read also:The Uglyest Person Alive Unveiling The Truth Behind The Label
Understanding the Basics of Java ArrayList
Before we jump into reversing ArrayLists, let's take a moment to understand what an ArrayList actually is. Think of it as a dynamic array that can grow or shrink as needed. Unlike regular arrays, ArrayLists don't have a fixed size, making them super flexible for storing and managing data. And guess what? They're part of the Java Collection Framework, which means they come with a ton of built-in methods to help you manipulate and manage your data like a pro.
Why Use ArrayList in Java?
Here's the deal: ArrayLists are awesome because they handle memory management for you. Need to add more elements? No problem. Want to remove an item? Easy peasy. Plus, they offer a bunch of useful methods for sorting, searching, and—you guessed it—reversing. If you're working with a collection of items that might change in size, ArrayLists are your go-to choice.
Java ArrayList Reverse: The Basics
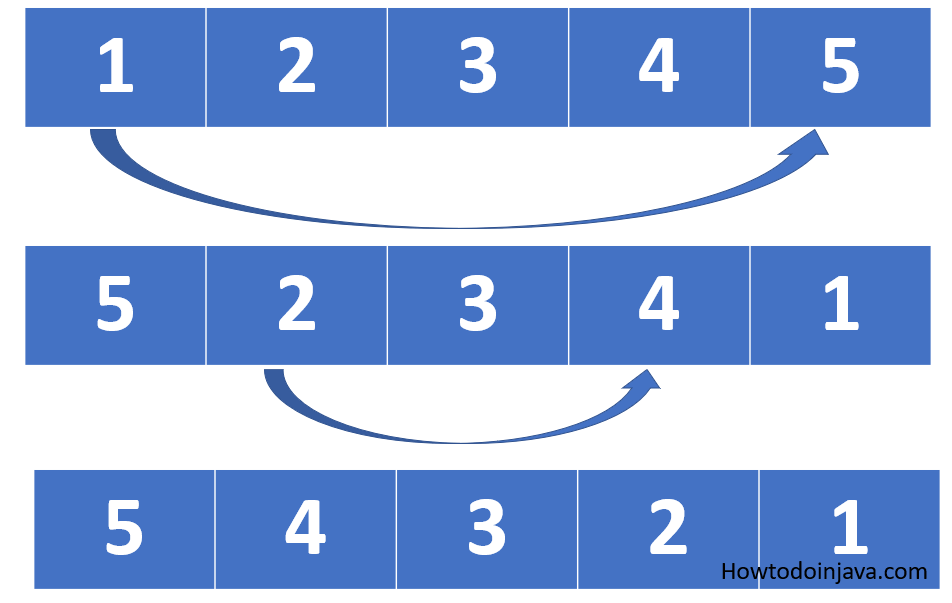
Alright, let's talk about the main event—reversing an ArrayList in Java. There are several ways to do this, and we'll explore them all. But first, let's break down what reversing an ArrayList actually means. Essentially, you're flipping the order of the elements so that the last item becomes the first, the second-to-last becomes the second, and so on. Simple, right? Well, as with most things in coding, there's more than one way to skin this cat.
Method 1: Using Collections.reverse()
This is probably the easiest and most straightforward way to reverse an ArrayList in Java. The Collections class comes with a handy method called reverse() that does exactly what it says on the tin. All you need to do is pass your ArrayList to this method, and voilà—it's reversed. Here's a quick example:
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
list.add("Cherry");
System.out.println("Original List: " + list);
Collections.reverse(list);
System.out.println("Reversed List: " + list);
}
}
See how easy that was? The Collections.reverse() method is perfect for situations where you just need a quick and reliable way to flip your ArrayList.
Read also:Tom Oakley Net Worth A Deep Dive Into The Success Story Behind The Numbers
Custom Reversal: Building Your Own Logic
Now, what if you want to get your hands dirty and build your own reversal logic? Sure, Collections.reverse() is great, but sometimes you might need more control over the process. Let's explore how to reverse an ArrayList manually.
Method 2: Using a Loop
This method involves iterating through the ArrayList and swapping elements from the start and end until you reach the middle. It's a bit more involved, but it gives you full control over the reversal process. Here's how you can do it:
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
list.add("Cherry");
System.out.println("Original List: " + list);
reverseList(list);
System.out.println("Reversed List: " + list);
}
public static void reverseList(ArrayList> list) {
int n = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i Object temp = list.get(i);
list.set(i, list.get(n - 1 - i));
list.set(n - 1 - i, temp);
}
}
}
See how we're swapping elements one by one? This method is especially useful if you're working with custom objects or need to add extra logic during the reversal process.
Advanced Techniques: Beyond the Basics
Once you've mastered the basics of reversing ArrayLists, it's time to level up your skills. There are a few advanced techniques you can use to make your code even more efficient and elegant.
Method 3: Using Streams in Java 8+
Java 8 introduced streams, which offer a powerful way to process collections of data. You can use streams to reverse an ArrayList in a single line of code. Here's how:
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList
list.add("Apple");
list.add("Banana");
list.add("Cherry");
System.out.println("Original List: " + list);
List
sorted((a, b) -> -a.compareTo(b)).
toList();
System.out.println("Reversed List: " + reversedList);
}
}
Streams are a game-changer for anyone working with collections in Java. They make your code concise, readable, and efficient.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
As with any coding technique, there are a few things to watch out for when reversing ArrayLists. Let's go over some common pitfalls and how to avoid them.
- Forgetting to Import Collections: If you're using Collections.reverse(), make sure you've imported the Collections class. Otherwise, your code won't compile.
- Modifying the Original List: Some methods, like Collections.reverse(), modify the original ArrayList. If you need to keep the original list intact, consider creating a copy before reversing.
- IndexOutOfBoundsException: When manually reversing an ArrayList, be careful not to go out of bounds. Always check the size of the list before accessing elements.
Real-World Applications of Java ArrayList Reverse
Now that you know how to reverse an ArrayList, let's talk about where you might use this skill in the real world. Here are a few examples:
1. Data Visualization
If you're working on a project that involves displaying data in reverse order, such as a leaderboard or a timeline, reversing an ArrayList can be incredibly useful.
2. Algorithm Design
Many algorithms, especially those involving stacks or queues, require you to reverse the order of elements. Knowing how to reverse an ArrayList can make these algorithms much easier to implement.
3. User Interfaces
In UI development, you might need to display items in reverse order based on user preferences. Reversing an ArrayList can help you achieve this with minimal effort.
Performance Considerations
When working with large datasets, performance becomes a critical factor. Let's take a look at how different reversal methods stack up:
- Collections.reverse(): This method is highly optimized and works well for most use cases. However, it modifies the original list, which might not always be desirable.
- Custom Loop: While this method gives you more control, it can be slower for very large ArrayLists due to the overhead of swapping elements.
- Streams: Streams offer a concise and elegant way to reverse an ArrayList, but they can be slower than other methods for large datasets.
Conclusion
And there you have it—your ultimate guide to mastering Java ArrayList reverse. Whether you're using Collections.reverse(), building your own logic, or leveraging streams, you now have the tools to reverse ArrayLists like a pro. Remember, the key to becoming a great developer is practice, so don't be afraid to experiment with these techniques and see what works best for your projects.
Before you go, I'd love to hear your thoughts. Have you used any of these methods before? Do you have a favorite way to reverse an ArrayList? Drop a comment below and let's keep the conversation going. And if you found this guide helpful, don't forget to share it with your fellow coders. Happy coding, and see you in the next one!
Table of Contents
Article Recommendations